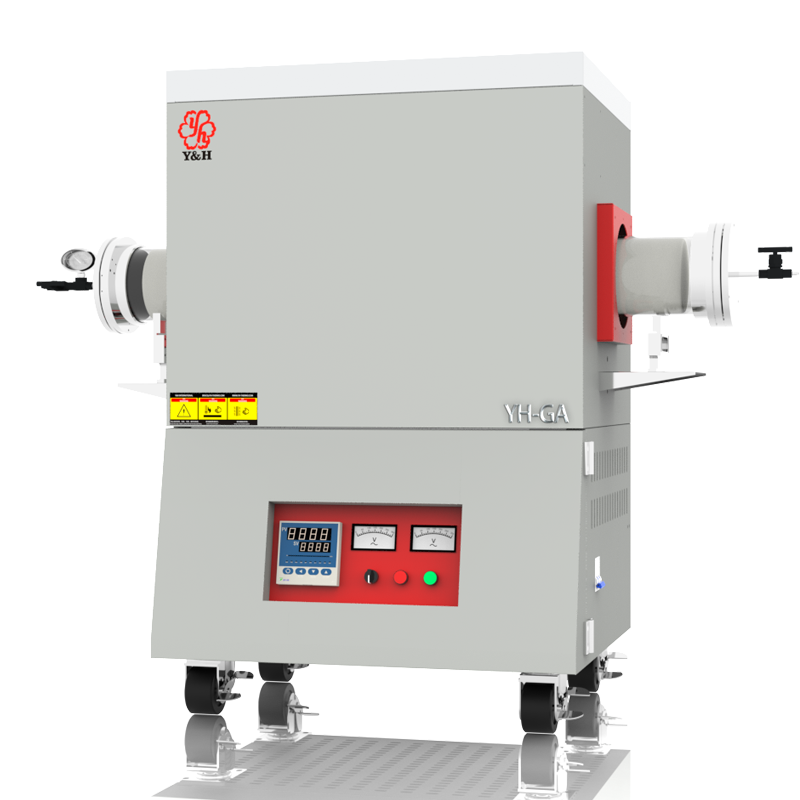
A tube furnace is a type of heating device characterized by the use of resistance heating elements to provide heat. These heating elements are typically made of alloy resistance wire, silicon carbide rods, silicon molybdenum rods, etc. The furnace tube is commonly made of materials such as metal, quartz, ceramic, or silicon carbide. Tube furnaces are typically designed in vertical or horizontal configurations. By applying electrical power, the heating elements generate high temperatures, heating the furnace tube to the desired temperature inside the furnace.


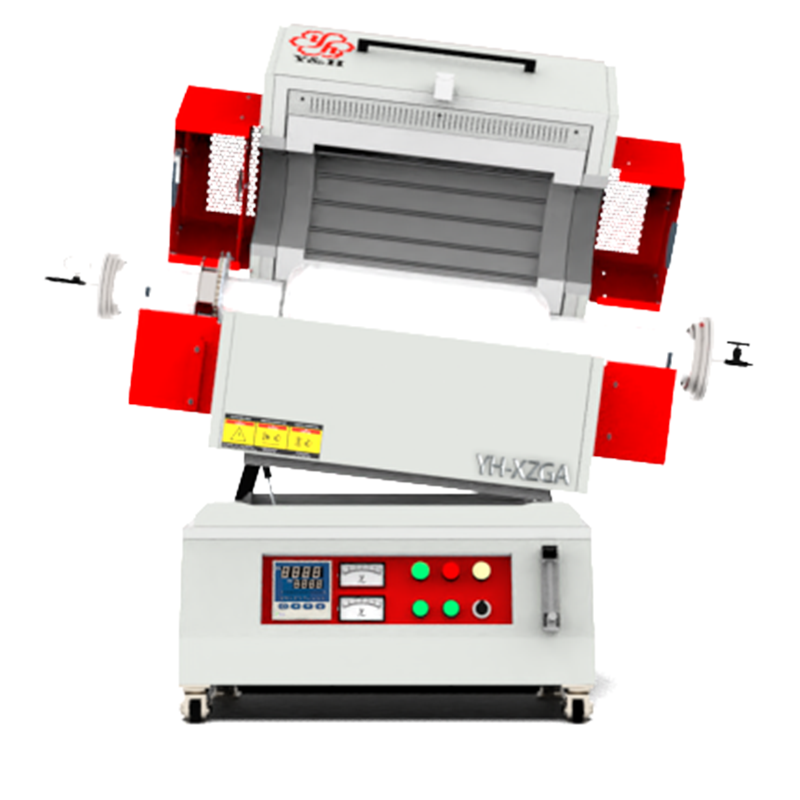
The tilted rotating tube furnace combines the design features of tilting and rotation to achieve uniform heating and heat transfer within the tube. This design not only ensures uniform temperature distribution inside the tube but also enhances heating efficiency and energy utilization. Suitable for heating materials of various shapes and sizes, the tilted rotating tube furnace is widely utilized in industrial applications such as powder drying, sintering, and more, providing efficient, precise, and energy-saving heating solutions for production processes.
Tube furnace tubes are typically made of materials such as stainless steel (0-1000°C), ceramics (1300-1700°C), silicon carbide (0-1400°C), or quartz glass (0-1150°C). These materials possess high temperature resistance and chemical corrosion resistance, making them suitable for various industrial and laboratory applications requiring high-temperature treatment or chemical reactions. The choice of material depends on factors such as the furnace tube's operating temperature, environmental corrosiveness, and mechanical strength to ensure safe operation and stable performance of the tube furnace.
Tube-type resistance heating furnaces find application in various industrial processes such as heat treatment (including annealing, tempering, and hardening of metals), sintering of powders, brazing, soldering, melting of metals, and curing of coatings and composites. These furnaces are prized for their ability to provide controlled and uniform heating environments, making them essential for industries requiring precise thermal processing capabilities.