
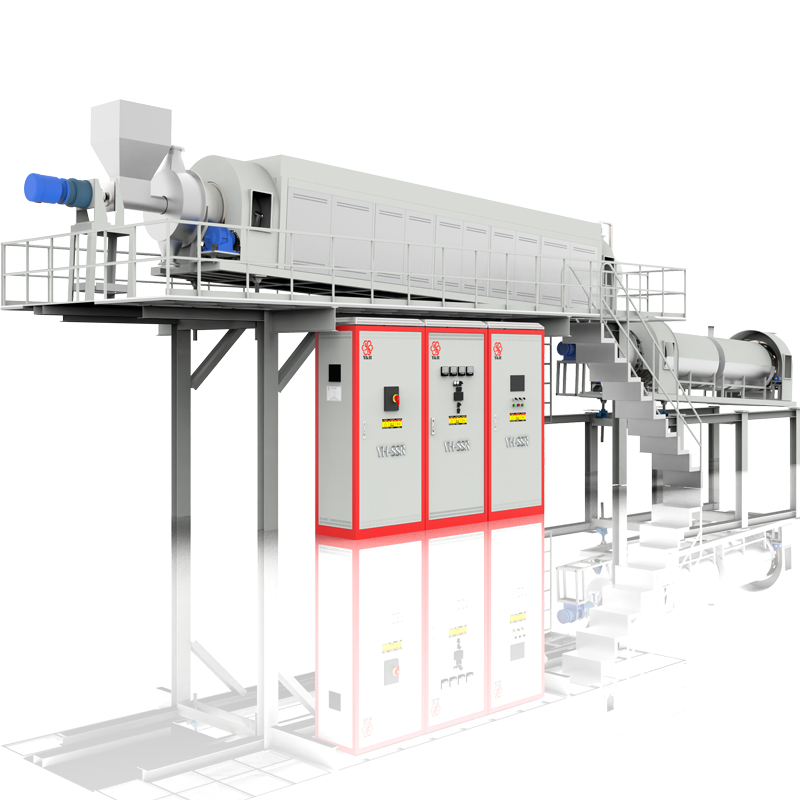
An electrically heated rotary kiln is an industrial equipment typically used for heating, calcining, or processing materials. It consists of a long, inclined metal cylinder that rotates within which materials are fed in at one end and move along the length of the cylinder as it rotates, undergoing heating in the process.
Electrically heated rotary kilns use electrical heating elements to raise the temperature inside the cylinder to the desired level. This heating method offers advantages such as precise temperature control, high efficiency, and environmental friendliness. It finds applications in various industrial processes including cement production, ore processing, chemical production,battery materials, etc., for purposes such as heating, drying, calcining, or thermal treatment of materials.


A rotary kiln typically consists of a feeding device, a furnace, an electrical control cabinet, and a kiln tube. Inside the furnace, there are supporting devices that can hold up the kiln tube. An electric motor drives a large gear to rotate the kiln tube. Materials enter from the feed end via the feeding device and pass through different zones such as the heating zone, calcining zone, and cooling zone to undergo the required processing.
Rotary kilns are widely utilized in industrial processes requiring thermal treatment or calcination of materials, including ceramics, powder particles, and other industrial production processes. They are extensively used in the production of cement, gypsum, lime, ceramics, and similar products. Rotary kilns are also employed in waste management and environmental industries for resource recovery.
A large rotary kiln is a heavy-duty industrial equipment typically used for the thermal processing, drying, or calcination of materials. It features a long cylindrical structure with one or more internal support devices, driven to rotate by an electric motor. The interior of the rotary kiln is typically divided into multiple zones, including material loading, heating, calcining, and cooling zones, where materials undergo various treatment processes. This equipment finds wide applications in industries such as cement production, metallurgy, chemical engineering, and environmental protection.