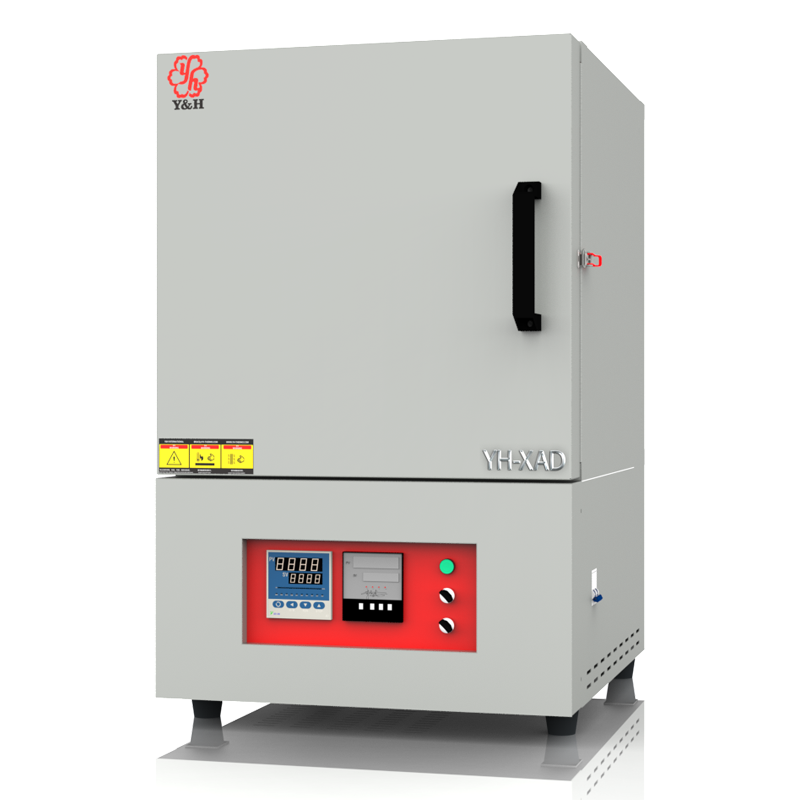
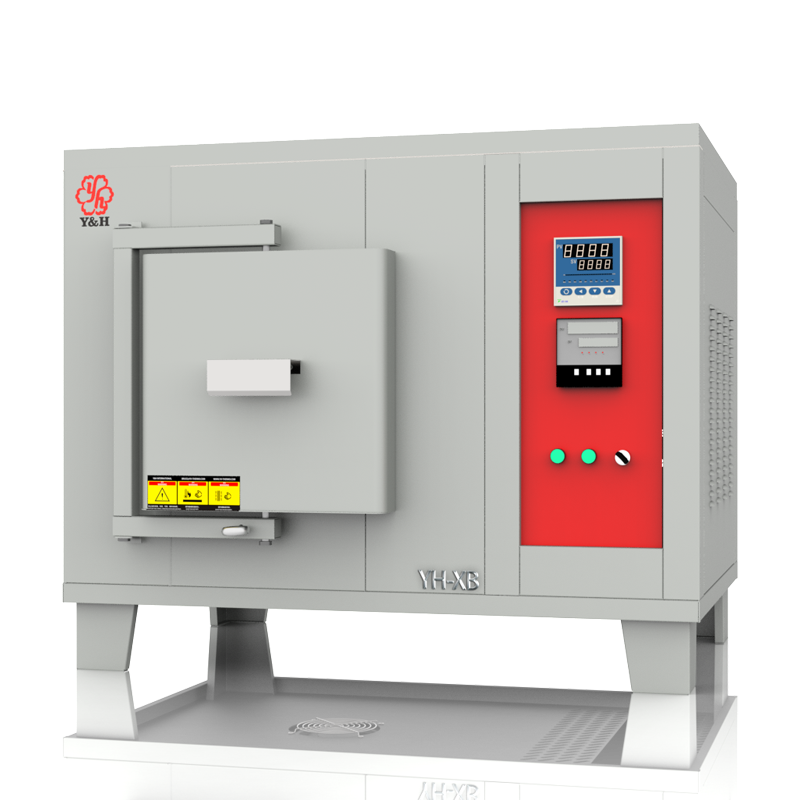
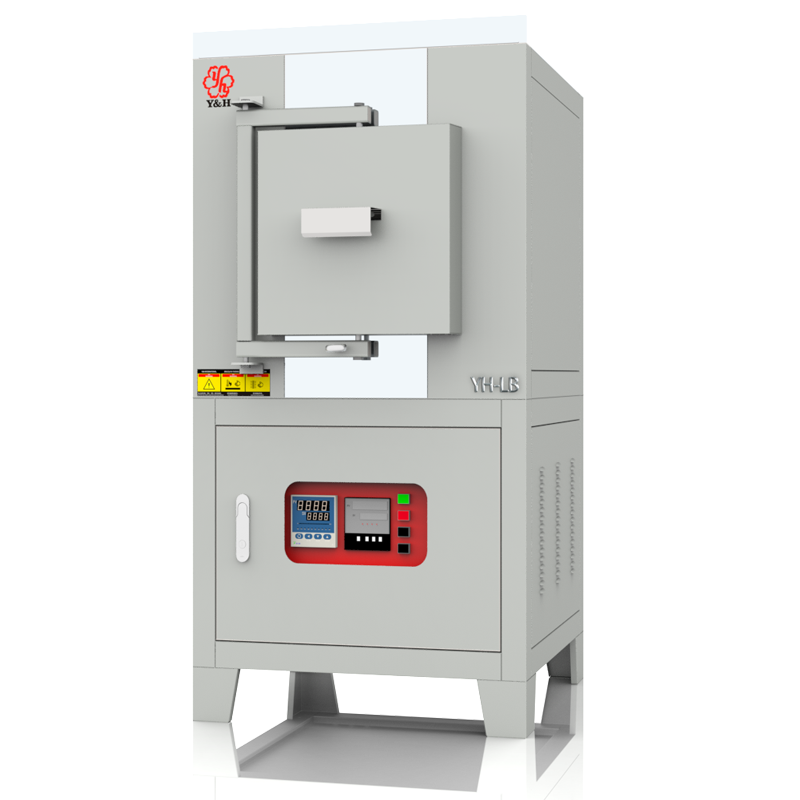
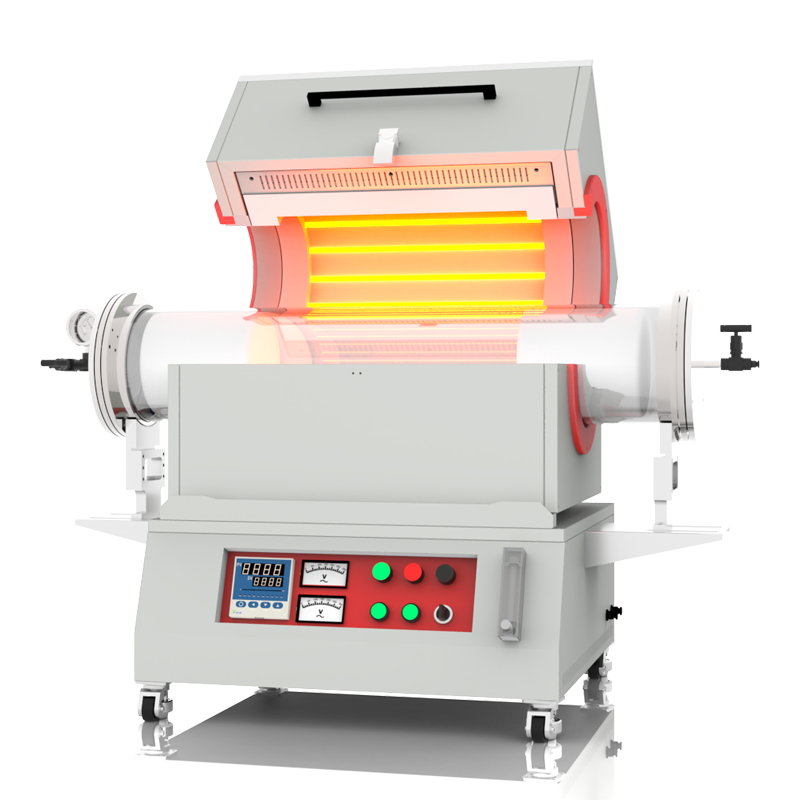
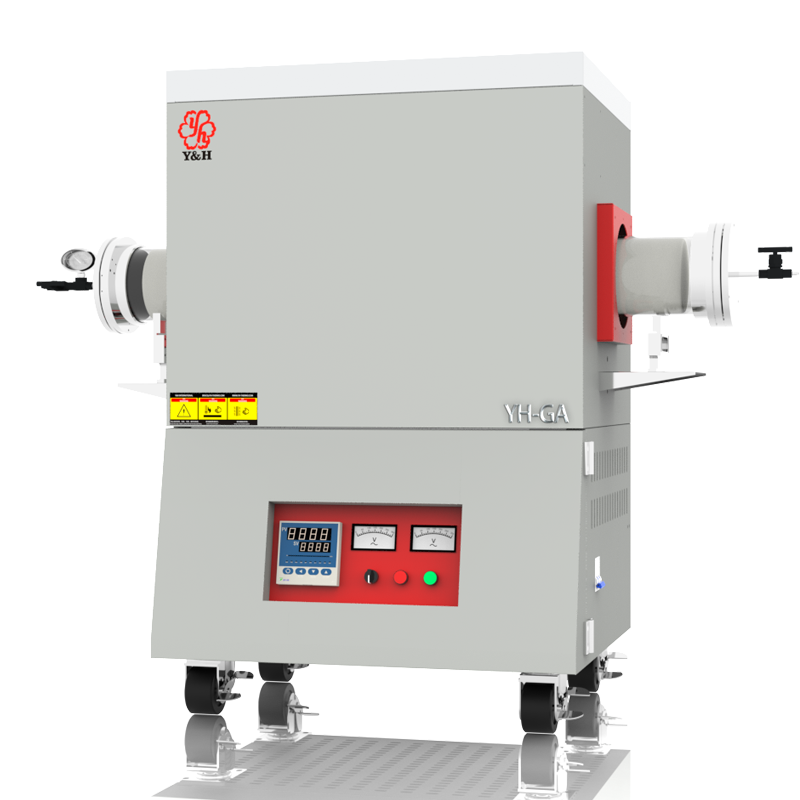
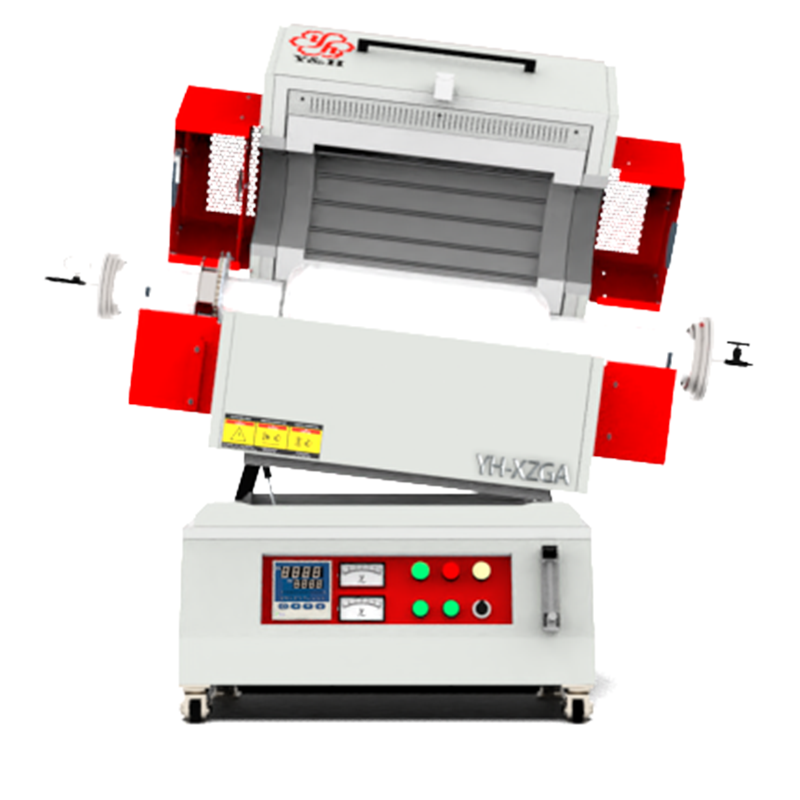
The application temperatures of crucibles or evaporating dishes vary with different materials.
Crucibles and evaporating dishes, as vessels used for high-temperature experiments and material processing, depend on the material type and manufacturing process for their heat resistance capabilities. Generally, fused quartz crucibles and alumina ceramic crucibles can withstand temperatures of over 1300 degrees Celsius, suitable for various high-temperature melting and chemical reactions. Graphite crucibles, known for their high heat resistance, can withstand temperatures up to 2500 degrees Celsius and are commonly used in experiments and processes requiring extremely high temperatures. Metal crucibles, depending on the specific metal type, have varying temperature resistance ranges and are used for specific high-temperature treatments and alloy melting. Evaporating dishes exhibit similar high-temperature stability in experiments and specialized treatments. When choosing, consideration of the material's heat resistance and chemical properties is crucial to ensure the vessel can safely and reliably withstand the required high-temperature environments.