YH-SS2
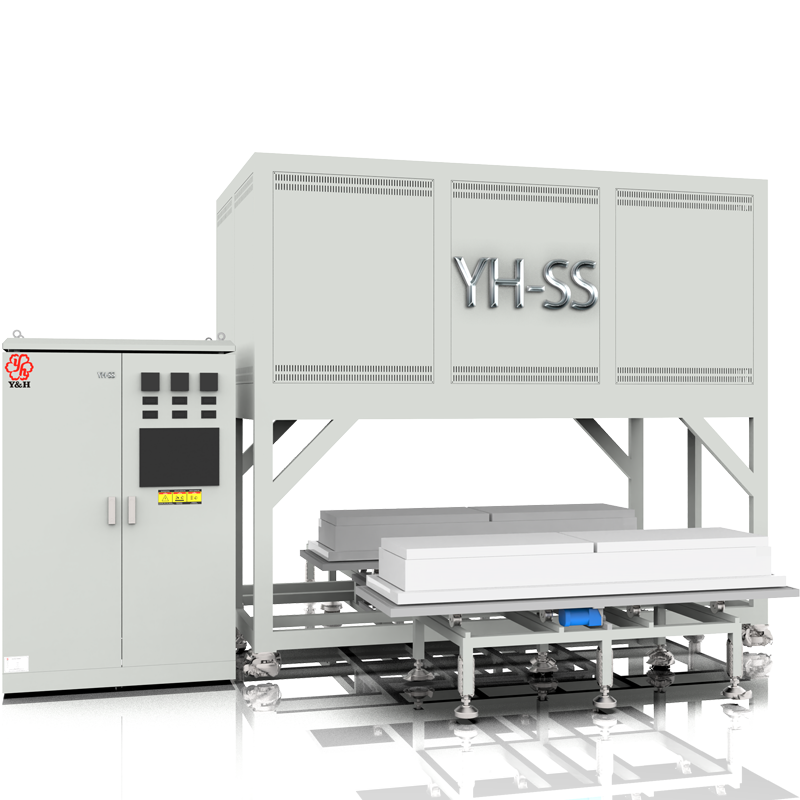
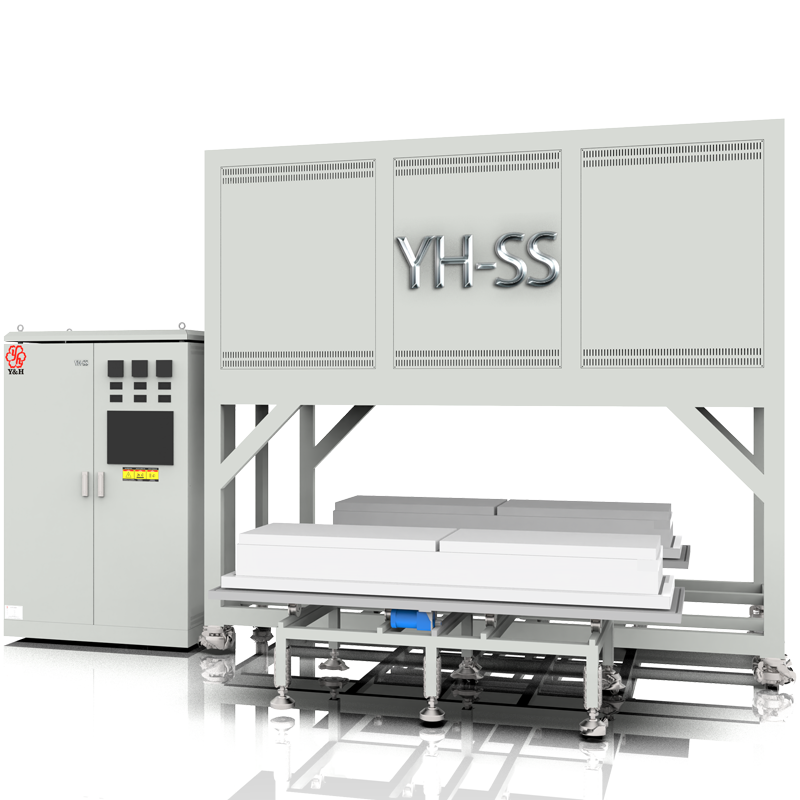
Bottom Loading furnace is an industrial device that combines resistance heating and lifting functions and has two charging tables. It is usually used in high-temperature treatment processes, such as metal smelting, glass manufacturing, ceramic production and other fields. Compared with traditional gas or liquid fuel heating methods, resistance heating elevating stoves have higher temperature control accuracy and cleaner working environment. And the loading and handling efficiency is higher.
The main components of the lifting furnace include:
Furnace Body (Chamber): The furnace body is the main part of the bottom lifting furnace, used to accommodate materials and provide heating space. It is typically constructed from ceramic fiber materials (plates, blankets, etc.) to withstand high temperatures and chemical corrosion. In addition to ceramic fiber materials, wear-resistant materials such as hollow sphere bricks are also chosen for the bottom platform to ensure long-term quality stability.
Heating Elements: Heating elements provide heat energy inside the furnace chamber to heat the material to the desired target temperature, ranging from around 1200°C to 1700°C. They are typically made of resistance wires (belts), silicon carbide rods, or silicon molybdenum rods.
Bottom Lifting Mechanism: The bottom lifting mechanism is one of the key components of the bottom lifting furnace, used to adjust the height of the furnace bottom. Through the lifting mechanism, the distance between the material and the heat source can be controlled, thus adjusting the heating time and temperature of the material. The lifting mechanism typically consists of hydraulic systems and screw rods. The bottom platform adopts a ladder-like structure, which fits with the furnace chamber, saving energy and insulation while reducing heat loss and improving sealing effectiveness.
Control System: The control system monitors and regulates the operation of the bottom lifting furnace, including parameters such as temperature, pressure, and lifting speed. Temperature control is usually achieved by temperature controllers, and the lifting movement is controlled by variable frequency drives. Large-scale lifting furnaces are equipped with touchscreen controls to improve production and control efficiency.
Optional Features:
Customizable Control Modes: Control modes can be customized from traditional domestic PID control to imported instruments or PLC control, providing various options to meet different customer preferences.
Platform Entry and Exit: Platform entry and exit can be customized for automatic movement, with a maximum of two platforms to facilitate loading and unloading while firing on one side.
Multi-Sided Heating: Depending on the furnace size, in addition to ensuring furnace temperature uniformity as much as possible, additional options for multi-sided heating are provided to meet higher requirements for furnace temperature uniformity.
Multi-Point Temperature Control: Depending on different usage scenarios, customers can choose multi-sided heating to improve heat radiation efficiency and expand the coverage of furnace temperature.
Exhaust Ports and Gas Paths: Exhaust ports, gas paths, and flow meters can be added according to customer requirements to meet process requirements (without vacuum sealing structure).
Touchscreen Control: Y&H can produce touchscreen control systems based on popular industrial touchscreen interfaces in the market, allowing real-time observation, report generation, and data download.
Standard specification
Product | Temperature Range(℃) | Chamber Dimension(mm) |
Bottom Loading Furnace | 1200-1700 | 200×200×200 |
300×300×300 | ||
500×500×500 | ||
800×500×500 | ||
800×800×800 | ||
1300×700×600 | ||
1000×1000×1000 | ||
1500×800×800 | ||
2000×800×800 | ||
3000×800×800 | ||
5000×800×800 | ||
Remark |
| |