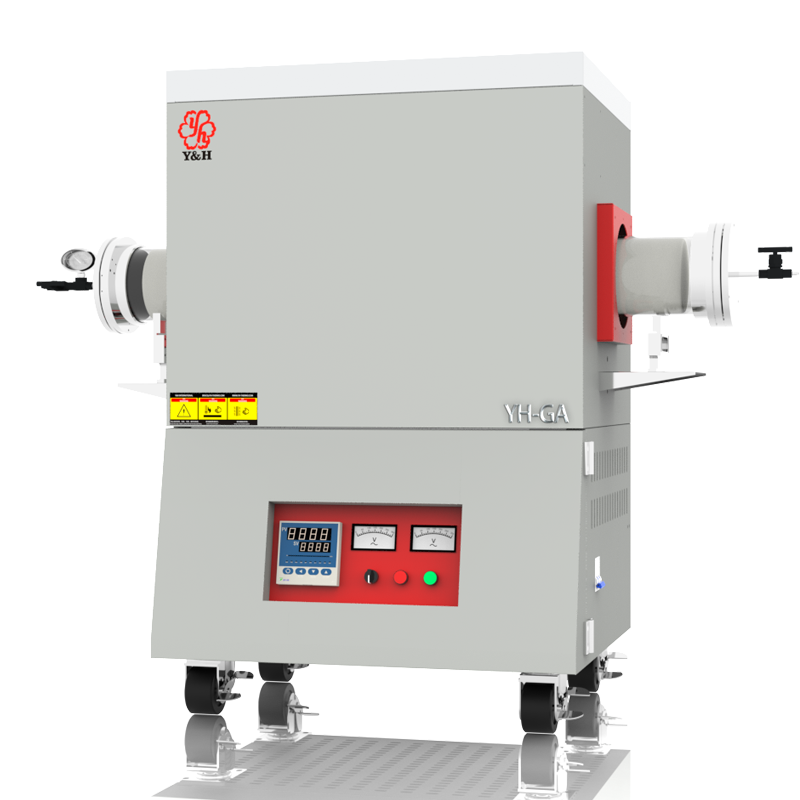
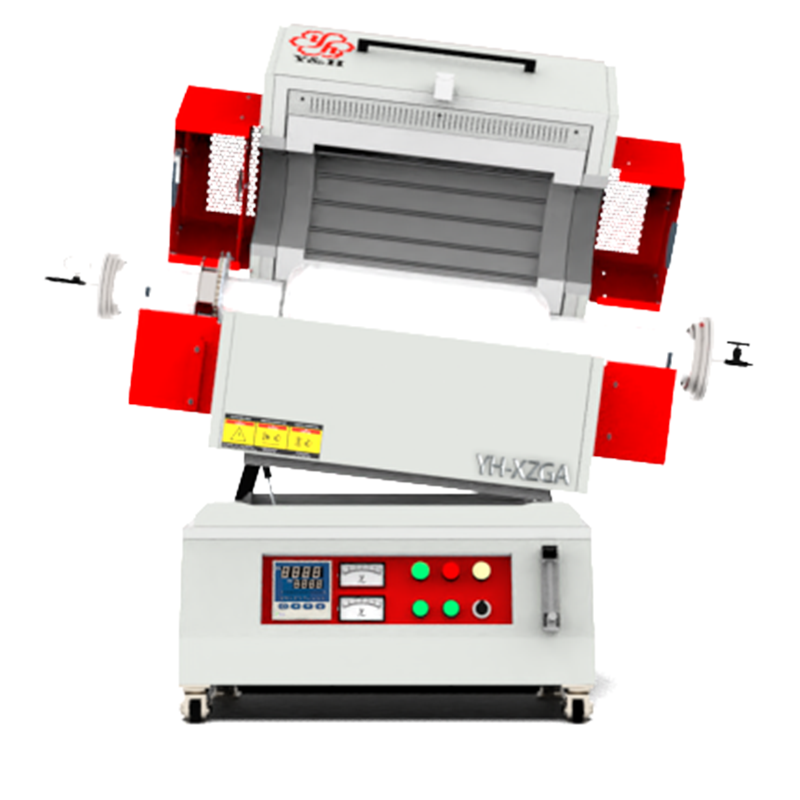
Does the atmosphere affect the heating efficiency of the resistance heating element?
Different atmospheric conditions, such as oxidizing, reducing, or inert atmospheres, significantly affect the heating efficiency and stability of resistance heating elements. In oxidizing atmospheres like air, elements may oxidize or degrade at high temperatures, impacting long-term heating performance. In reducing atmospheres (e.g., hydrogen or hydrocarbon gases), chemical reduction can alter the material's resistance or induce reactions that affect heating capabilities. Conversely, inert atmospheres (e.g., nitrogen or argon) typically maintain stable conditions for the elements, avoiding chemical reactions or oxidation. Therefore, selecting and using resistance heating elements involves considering the atmospheric conditions of the operational environment to ensure stable and efficient heating performance.